Most people describe diamonds as *white*, standard typical diamonds that we see in our daily lives.
But this is wrong for 2 reasons:
1. White color s actually well…..White! And therefore is not the color of the typical diamonds, because they are transparent.
2. White diamonds fall in the colored diamonds category, also called fancy color diamonds in the trade (pictures below).
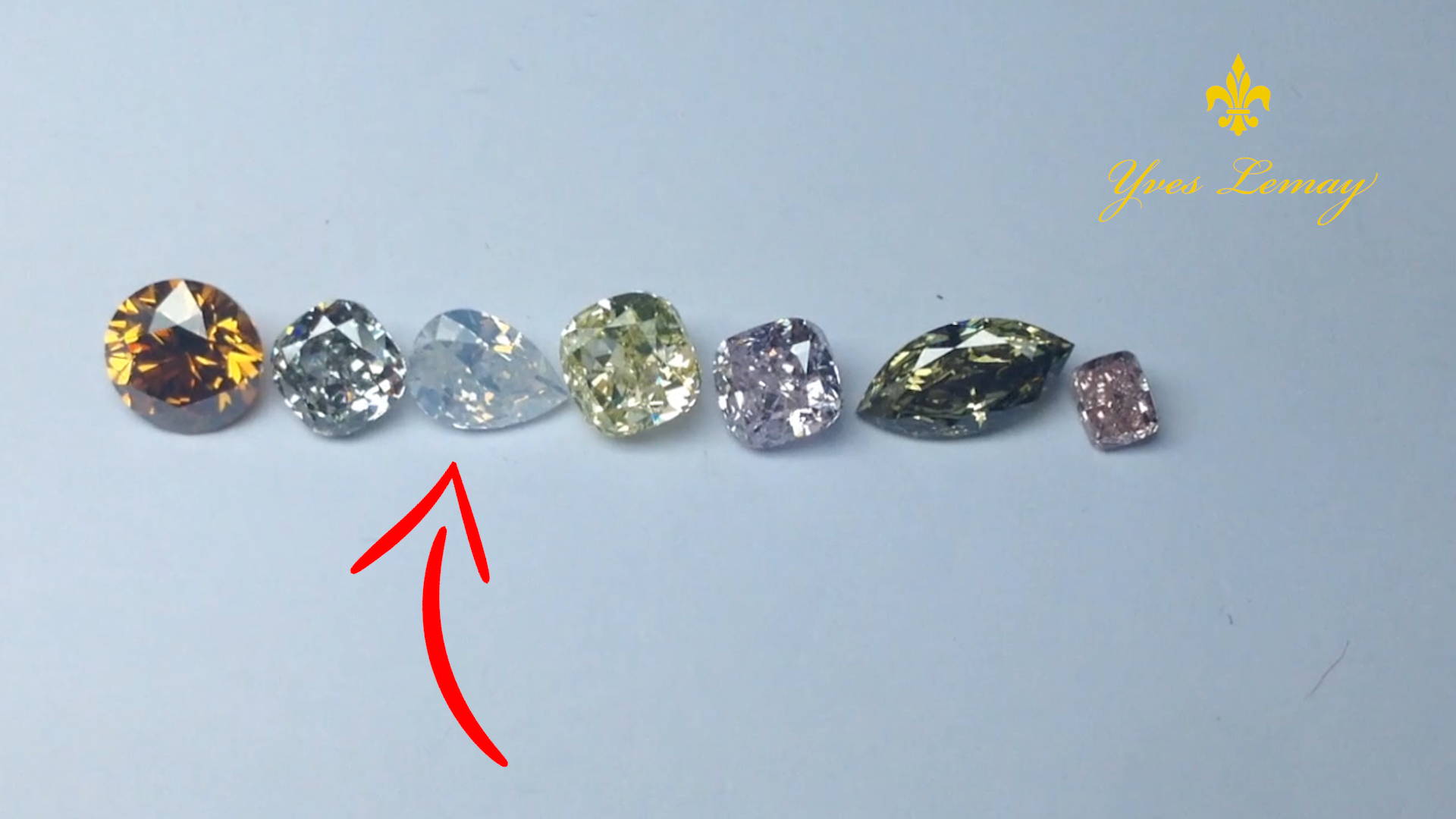
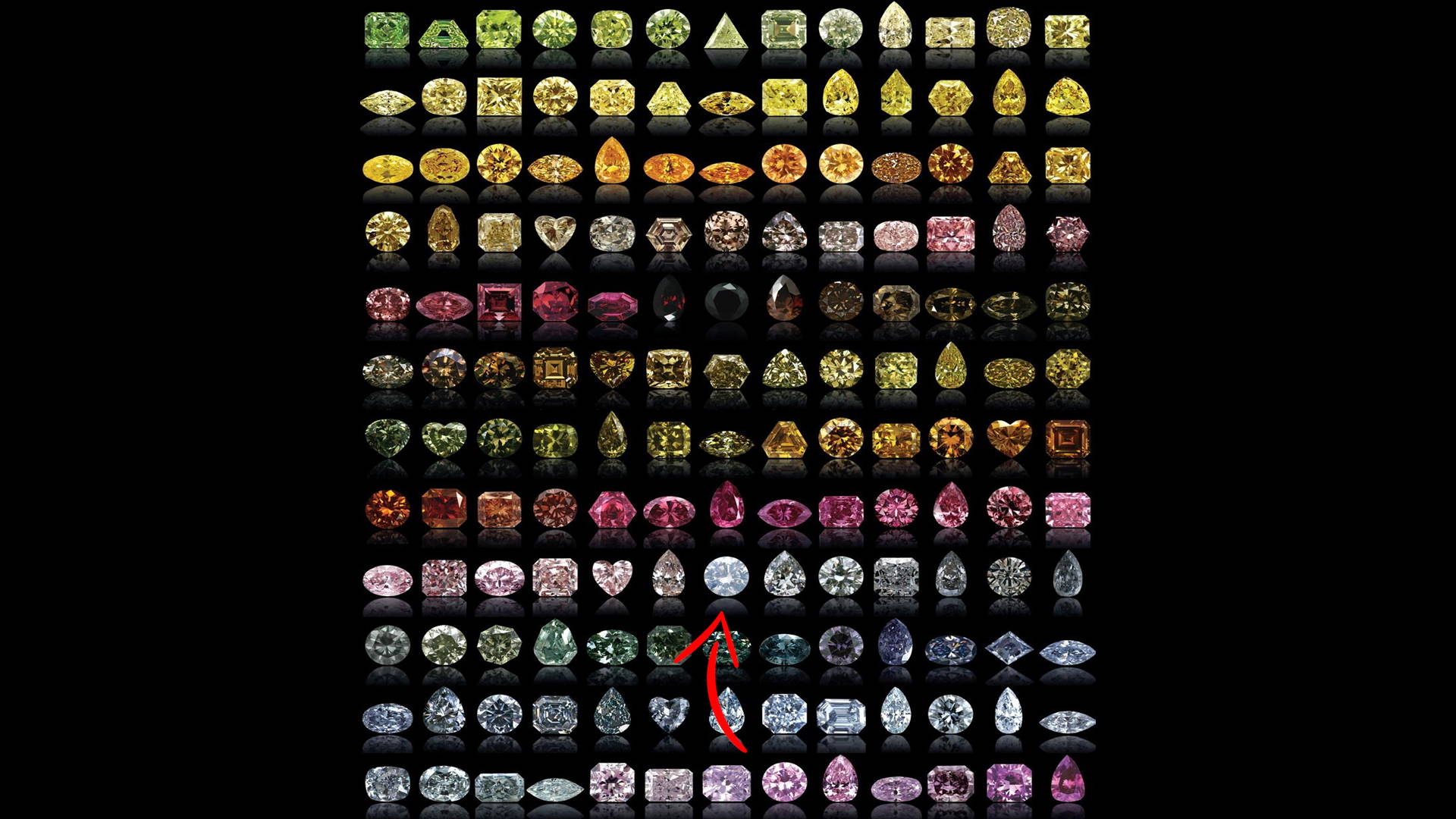


Now that we got that straight, we will describe typical diamonds as colorless.
The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) grades the colors of the colorless diamonds from D to Z. (Where D is totally colorless, higher value diamond and Z is light yellow, less value diamond).
These grades are divided into categories below:
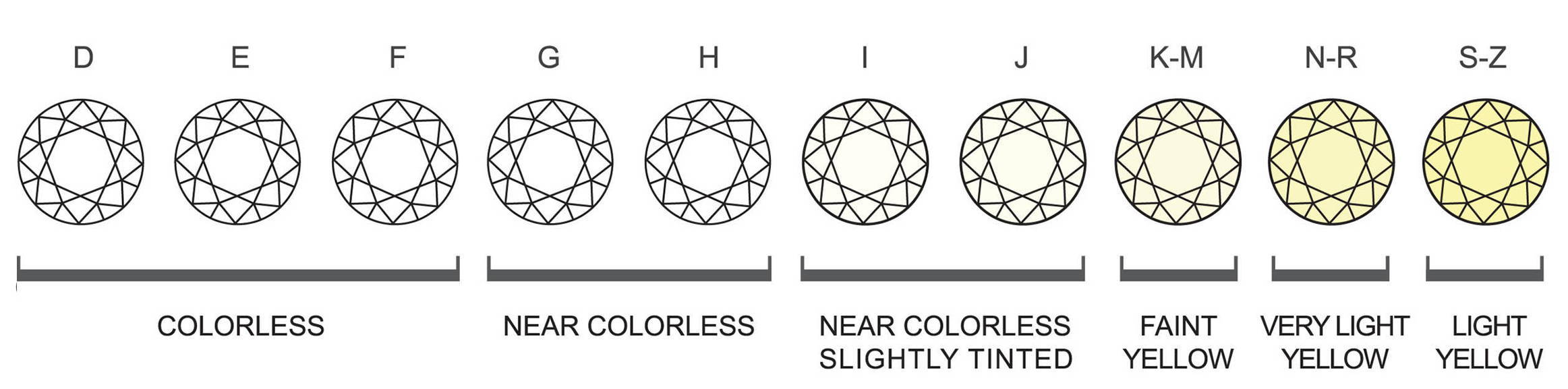
The 2 categories that interest us the most are Colorless and Near Colorless.
However, D, E, F grades significantly increase the value of the diamond.
As you know, the purpose of the engagement ring is to be worn daily; how much do you think your fiancé will appreciate such diamonds’ colorlessness?
Yeah, you are starting to get my point…
The sweet spot that I found out after serving hundreds of clients throughout my 20 years of experience is G and H colors.
Most people will not see any color in such grades of diamonds, especially if you do not present them next to D, E, F grades.
But at the end of the day, the price difference is pretty significant.
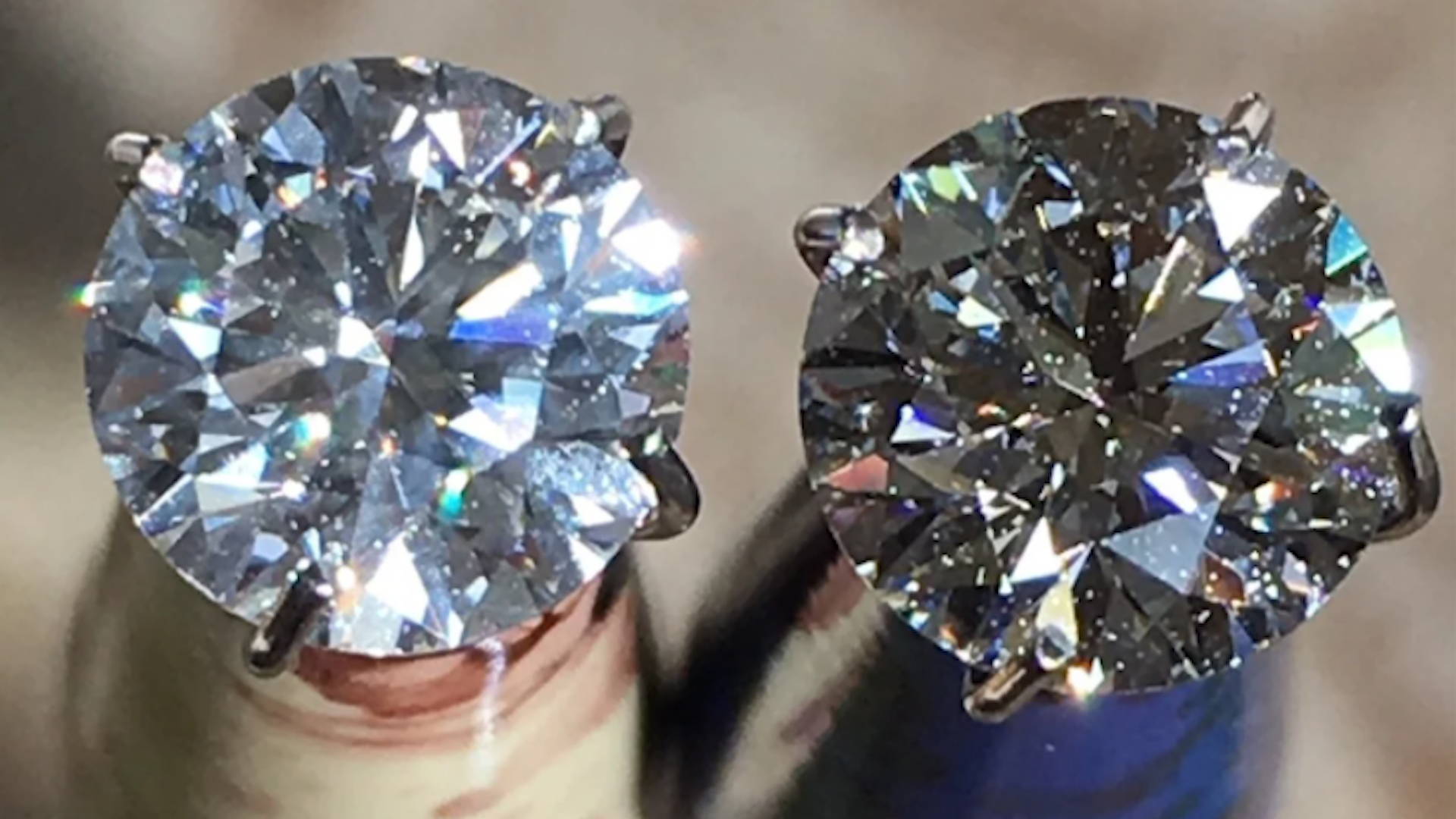
Another trick related to that is not to be afraid to purchase a diamond that has Blue Fluorescense.
In fact, one-third of all diamonds, when exposed to UV light, will exhibit a certain color of fluorescence at a certain degree of intensity (from Faint to Very Strong).
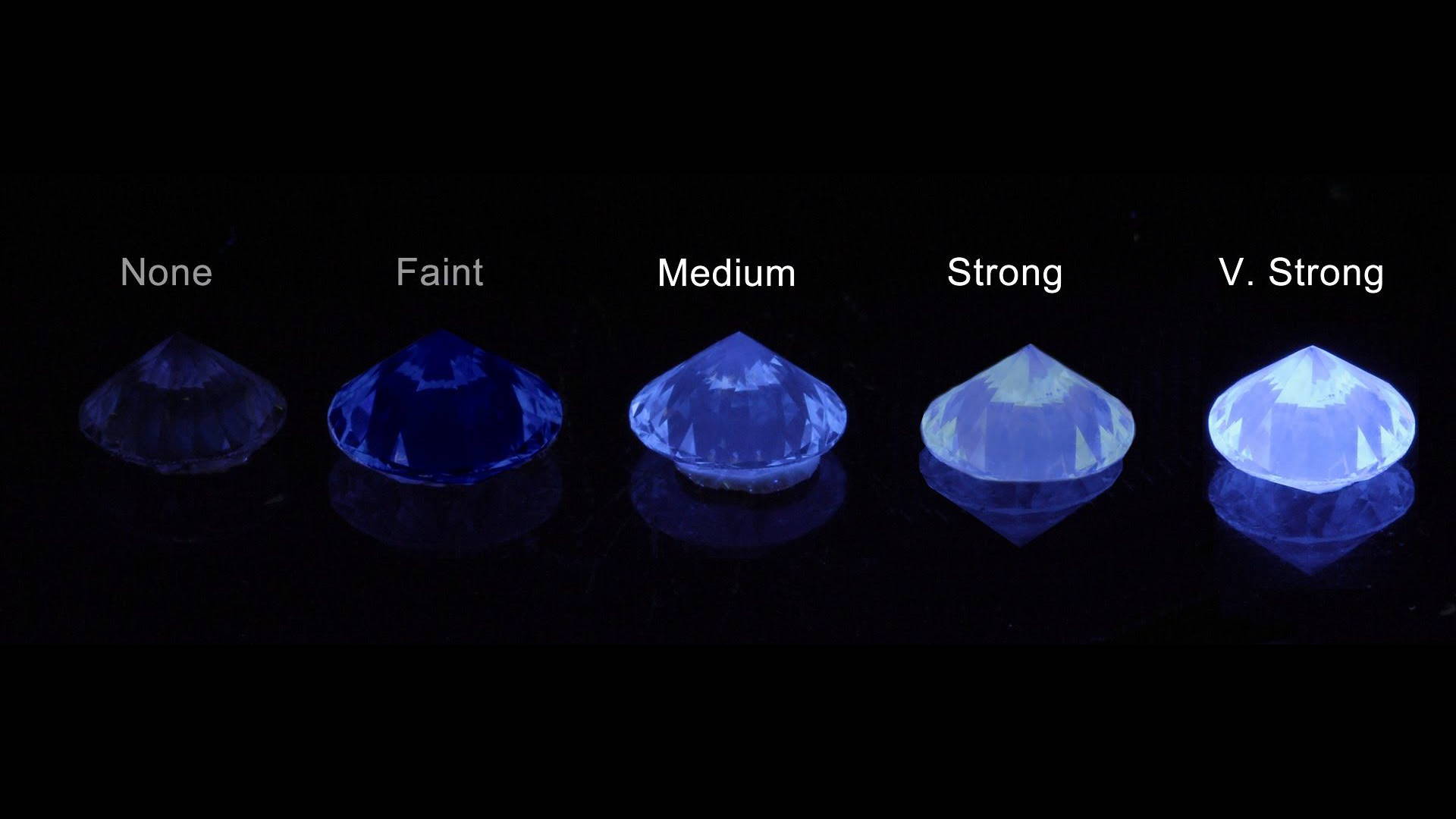
While the vast majority of such diamonds will show absolutely no difference under regular sunlight, some diamonds at Strong and Very Strong level of fluorescence will appear milky or hazy (picture below).
These should be avoided.

As we can see here below, color mixing in pigment or paint, which is also called subtractive synthesis, doesn`t work the same way as color mixing in light, called additive synthesis.
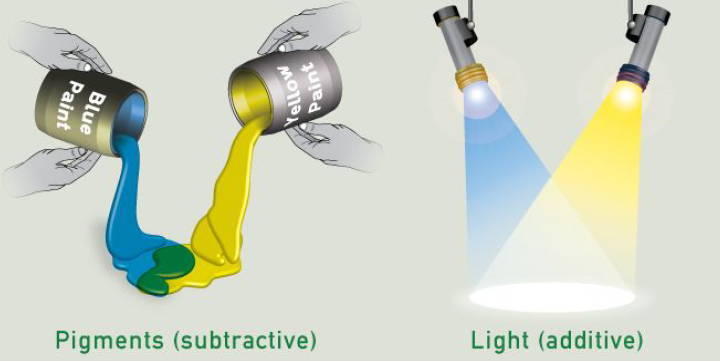
Blue and yellow are opposite in additive synthesis.
So if you will go for a Medium or Strong fluorescence diamond, that will help to counterbalance the G and H color grade, which will make overall under sunlight your diamond look a little bit more colorless.
Boom!
So you pay less for a Near Colorless grade of diamond G and H, you pay less because of the fluorescence presence, and you will end having a diamond that is even better.